Introduction
The Excel IRR skill practice is a must-have for finance professionals, analysts, and business leaders. The Internal Rate of Return (IRR) is one of the most important financial metrics used to evaluate investment opportunities and measure project profitability.
In Excel, you can calculate IRR with two key functions:
- IRR – works for evenly spaced cash flows (annual, quarterly, monthly).
- XIRR – works for irregularly spaced cash flows with exact dates.
By mastering IRR and XIRR in Excel, you can quickly determine whether an investment adds value, compare projects, and make smarter financial decisions.
What is IRR and XIRR in Excel?
IRR (Internal Rate of Return) in Excel
The IRR is the discount rate at which the Net Present Value (NPV) of cash flows equals zero. It is best suited for projects with evenly spaced intervals, such as annual or quarterly returns.
Formula in Excel:
=IRR(values)
XIRR (Extended Internal Rate of Return) in Excel
The XIRR is a more advanced version of IRR. It considers exact dates for cash flows, making it ideal for irregular investments, venture capital funding, or real estate projects.
Formula in Excel:
=XIRR(values, dates)Why Excel IRR Skill Practice is Essential
- Evaluate project profitability before approvals.
- Compare investment opportunities across industries.
- Calculate venture capital or private equity returns.
- Assess real estate project IRRs.
- Perform scenario and break-even analysis.
Example Dataset for Excel IRR Skill Practice
| Project | Date | Cash Flow |
|---|---|---|
| A | 01-Jan-2020 | -20000 |
| A | 01-Jan-2021 | 8000 |
| A | 01-Jan-2022 | 10000 |
| A | 01-Jan-2023 | 12000 |
| B | 01-Mar-2020 | -25000 |
| B | 01-Sep-2020 | 6000 |
| B | 01-Mar-2021 | 7000 |
| B | 01-Mar-2022 | 15000 |
| C | 01-Apr-2020 | -30000 |
| C | 01-Apr-2021 | 12000 |
| C | 01-Oct-2021 | 10000 |
| C | 01-Apr-2022 | 15000 |
20 Excel IRR / XIRR Skill Practice Problems with Solutions
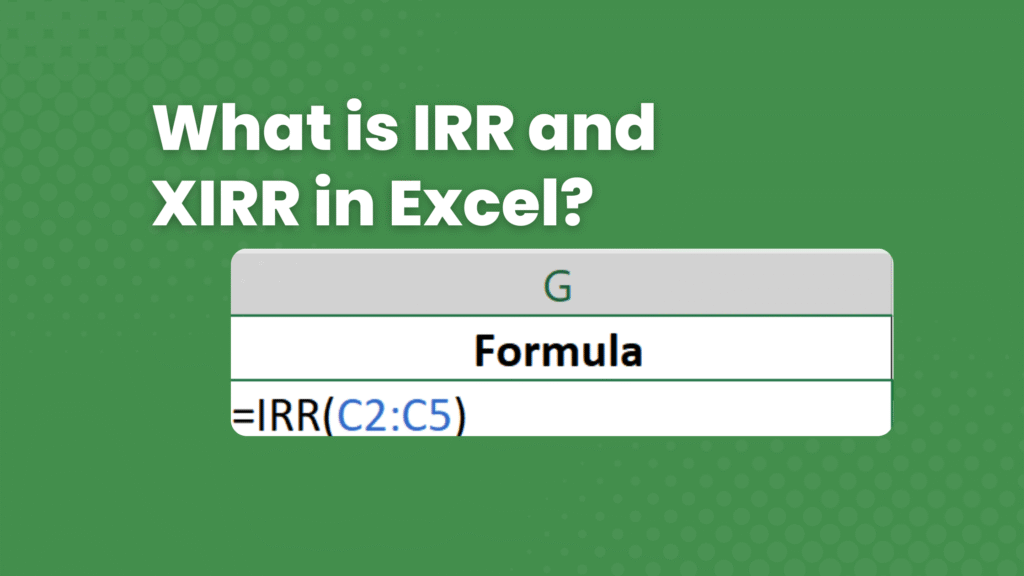
- Calculate IRR for Project A using annual cash flows
=IRR(C2:C5)→ 19.43% - Calculate IRR for Project B
=IRR(C6:C9)→ 15.20% - Calculate IRR for Project C
=IRR(C10:C13)→ 10.84% - Use XIRR for Project A with exact dates
=XIRR(C2:C5,B2:B5)→ 18.75% - Use XIRR for Project B with exact dates
=XIRR(C6:C9,B6:B9)→ 14.98% - Use XIRR for Project C with exact dates
=XIRR(C10:C13,B10:B13)→ 10.52% - Compare IRR vs. XIRR for Project A
- IRR = 19.43%
- XIRR = 18.75%
- Add an initial investment of $30,000 to Project A
=IRR({-30000,8000,10000,12000})→ 7.70% - Modify Project B: include negative Year 2 cash flow (-2000)
=IRR({-25000,6000,-2000,15000})→ 8.91% - Monthly cash flows: -10000, 2000 (x6), 3000 (x6)
=IRR({-10000,2000,2000,2000,2000,2000,2000,3000,3000,3000,3000,3000,3000})→ 11.65% - Quarterly cash flows: -50000, 15000, 18000, 20000
=IRR({-50000,15000,18000,20000})→ 13.82% - Terminal value of $50,000 at Year 5 for Project A
=IRR({-20000,8000,10000,12000,50000})→ 43.19% - Scenario analysis: Optimistic case (20% higher inflows for Project A)
IRR → 26.42% - Scenario analysis: Pessimistic case (15% lower inflows for Project B)
IRR → 7.86% - Compare IRRs of Projects A, B, and C – best project
Project A (19.43%) > Project B (15.20%) > Project C (10.84%) - Combined IRR for Projects A + B
=IRR({-45000,14000,17000,27000})→ 16.92% - Break-even discount rate for NPV = 0 (use Goal Seek for Project A)
IRR → 19.43% - Irregular inflows: -20000, 5000, 7000, 10000, 12000
=IRR({-20000,5000,7000,10000,12000})→ 14.79% - Compare IRR vs. NPV for Project B (12% discount rate)
- IRR = 15.20%
- NPV = 2,707.03
- Advanced XIRR for mixed irregular dates and cash flows
=XIRR({-25000,6000,7000,15000},{01-Mar-2020,01-Jul-2020,15-Mar-2021,30-Dec-2022})→ 14.55%
Conclusion: Building Your IRR and XIRR Skills in Excel
The Excel IRR skill practice is a must-learn for professionals working in finance, investments, and project management. By mastering IRR and XIRR, you gain the ability to assess project profitability, compare opportunities, and support smarter business decisions.
For a deeper understanding of the Internal Rate of Return (IRR) and its role in financial analysis, you can read this detailed guide on Investopedia.
Related Topics
- EDATE Skill Practice – Shifting dates by months (loan maturity, billing cycles).
- EOMONTH Skill Practice – Finding month-end dates for cash flow forecasts.
- TODAY / NOW Skill Practice – Using dynamic current date/time in aging reports.
- TEXT Skill Practice – Formatting numbers, dates, and percentages professionally.
- CONCAT / TEXTJOIN Skill Practice – Combining text strings for reports and IDs.


